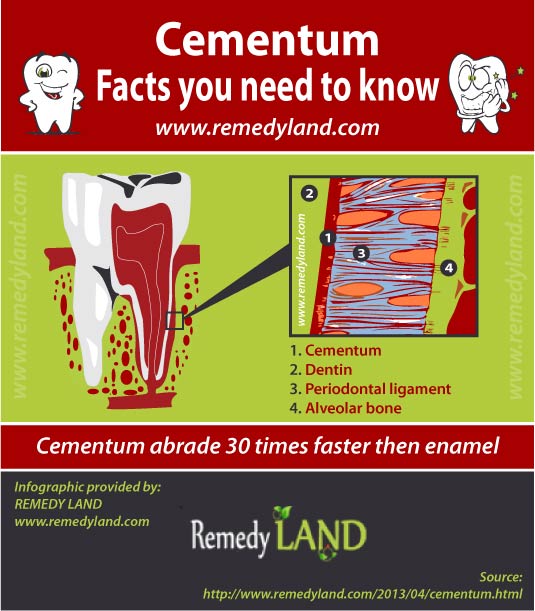
Cementum
Cementum is the element of a tooth, the layer of stiff connective structure below the gumline, overlaying the tooth root. It is actually thickest at the ground level of the tooth. The main purposes of cementum are to preserve the root and help in keeping the tooth safely in the periodontal socket.
Cementum is the mineralized connective tissue similar to bone, that protects the roots of tooth and provides anchor to gum and gum fibers. Certain forms of cementum may additionally develop on top of the dental enamel of the tooth crown. In contrast to the bone, cementum isn’t vascular.
Cementum expands gradually on surface area, all through his existence. The biggest feature of cementum is the anchorage of tooth to the adjacent alveolar bone by the periodontal ligament. On the other hand, it provides additional capabilities also. Cementum is significantly less vulnerable to resorption compared to dentin. Even though it can easily be destroyed, cementum functions as a protecting coating over the teeth dentin. Continuing desublimation of cementum in the apical surface recompense for aggressive tooth wear at the tooth surface area.
Yellowish in tint, cementum possesses a dull exterior. It’s gentle compared to the dentine and enameled surface that covers the visible part of the tooth. The material of the gum membrane, the structure between the tooth, and the periodontal socket is embossed within the cementum. Since the tooth crown wears down with time, unique cementoblast tissues are encouraged to generate more cementum around the root.
Acellular cementum, afibrillar cementum, cellular cementum
The cementoblasts are made within the tooth pulp. Cells constantly produce new cementum due to the fact it’s not as strong as tooth enamel. By opposite, the tooth enamel is created just throughout fetal creation. The cells could quickly be worn out or demolished, and its substitution guarantees that the periodontal ligaments are constantly reinforced to keep the tooth safely in position through time. There exists three different forms of cementum.
- The acellular cementum includes around one third of the tooth right next to the boundary layer with the tooth enamel.
- Afibrillar cementum is a compact coating which could stretch from the acellular cementum onto the tooth enamel.
- The cellular cementum is the thickest coating, overlaying the bottom, two third of the tooth root.
The cementum regular growing method is dependent on the regular supplement of cementum, a unique calcified material deposited on the roots of tooth in most mammals. Deposits of cementum generate ring much like those in trees. A darkly discolored circle is created throughout winter, and while ring is created throughout spring and summer time.
The main threat to the health of the cementum is periodontal recession, which frequently happen over age forty five, because of constantly tough brushing or the first phases of periodontal condition. With periodontal recession, the periodontal tissue pulls out from the tooth and starts to reveal the cementum along with the tooth root. Cementum is thinnest part of the tooth, and that usually is the region that tooth gets revealed. That causes it to be seriously susceptible to erosion at the time of tooth brushing.
Interrelationships between the cementum and tooth enamel in males
Interrelationships between the cementum and tooth enamel in females
*Sample size 280 patients
Erosion of the cementum may lead to tooth tenderness, cause decomposition, and result in tooth root deterioration. Extreme deterioration of the cementum may lead to tooth loss as a result of the removal of the periodontal ligaments that maintain tooth in the position.
You may also like:
- How to stop gingival recession or receding gums treatment, causes,…
Gingival recession or receding gums, is a disorder in which the teeth roots come to be uncovered. Receding gums are common with patients with gingivitis.
- Dental crown pain – important facts you need to know…
Dental crown pain – important facts. Tooth crown pain is usually the consequence of dental crown that does not lay on the tooth properly.
- Dental erosion or tooth erosion facts, tips and treatment
Dental erosion is a long term acid damage of all or section of a tooth. Tooth erosion treatment and remedy is based on the level of tooth wear.