What is miosis? (definition)
Miosis or myosis a medical term referring to excessive constriction of the pupils, as a result of drugs or diseases. The non-medical term for pupillary miosis is constricted pupils or pinpoint pupils. Miotic pupils are condition opposite to mydriasis.
Page Contents
Pathophysiology of constricted pupils
The pupil is the black circle in the center of the eye. Its function is to control how much light gets in your eye. The size of the eye pupil is controlled by sphincter muscle of the iris and the iris dilator muscle. When the environment is bright your pupils are small, and when the environment is dark your pupils are large.
In order to protect eye from too much light your pupils are constricting or getting smaller. But when eyes need more light and to prevent eye strain, pupils are dilating or getting bigger. This is a normal function of the pupils and they are doing it thousands of time a day. Abnormal miosis happens when pupils stay constricted even in low light situations.
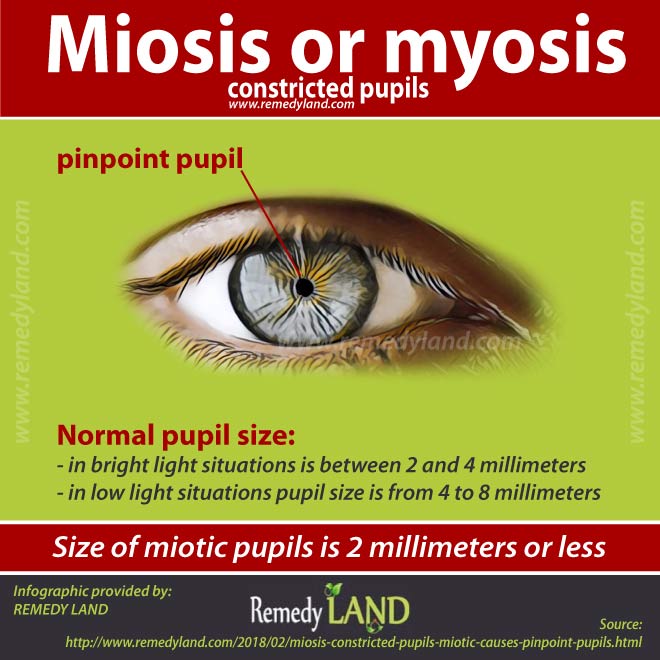
Size of pinpoint pupils
Normal pupil size in bright light situations is between 2 and 4 millimeters, but in low light situations pupil size is from 4 to 8 millimeters. Size of miotic pupils or pinpoint pupils is 2 millimeters or less, the problem is more obvious if the environment is dark. It is also important to know that miosis can happen in one or both eyes.
Diagnosis of the miotic pupils
Pupillary assessment is the best and the easiest way to determine abnormal pupillary miosis. There are few methods examiners can use to diagnose myosis and those are:
- Swinging flashlight test for constricted pupils is performed in dim room light. The patient is asked to look into the distance by examiner. The bright light is shone into eyes leads. The pinpoint pupils with an abnormal miotic tendencies does not change size, they stay constricted.
- Accommodation reflex test for pupillary miosis uses distance as the indicator. The examiner will instruct patient to look at a distant object and then he will gradually bring distant object within 5cm of the eyes. If pupils stay small and constricted during the test, abnormal myosis can be concluded.
What are the causes of constricted pupils?
Miosis is not a disease in itself, the pinpoint pupils are sign of underlying medical problems. If the person is healthy, miotic pupils can be reaction to the amount of light retina receives. Constricted pupils are usually product of complex mechanism that involves nerve cells and chemicals.
There are many factors that may cause miosis and those are:
Pupil constriction is normal for newborn’s because miosis is used as extra protection from bright light in first 2 weeks of life. Myosis also occurs as a person gets older, because the eye muscles get weak and slow, this is known as a senile miosis. Treatment for this kind of constricted pupils is unnecessary.
Iritis as a cause of pinpoint pupils
Even an inflammatory condition of the eye such as iritis can cause miosis. Iritis or anterior uveitis may be a consequence of trauma which can cause an inflammation of the iris. Besides constricted pupils symptoms of iritis are red eye, blurred vision, light sensitivity and sight loss. You must visit your doctor to prescribe you medications, the only thing you can do is to ware dark glasses and use medications exactly as prescribed.
Constricted pupils induced by drugs or medications
One of the most likely reasons behind pinpoint pupils is use of certain drugs or narcotic pain medications, because they stimulate nervous system and consequently constrict pupils. Only treatment for this kind of miosis is ceasing the use of these drugs.
Horner’s syndrome can cause unilateral miosis
This rare disease known as Horner’s syndrome can causes problems with one side of your face and one pupil. Horner’s syndrome affects eyes nerves known as the sympathetic trunk. One of the major symptoms of this disease is miotic pupil. Other major symptoms are droopy eyelid and loss of hemifacial sweating.
Pupillary miosis due to organophosphate poisoning
Over exposure to a large doses of organophosphates (insecticide) can cause poisoning. Constricted pupils are common in organophosphorus poisoning. Other symptoms are vomiting, salivation, diarrhea, abdominal pain … fecal incontinence.
Miotic pupils are symptom of brain hemorrhage
Intracerebral hemorrhage is bleeding in the brain tissue or ventricles. Bleeding is caused by an artery in the brain bursting because of trauma or high blood pressure. Pupil constriction is one of the symptoms besides headache, vomiting, seizures, difficulty swallowing, problems with vision … weakness in an arm or leg.
Hyperopia as a cause of myosis
Farsightedness or hyperopia is a condition that occurs when the eyeball is too short. People with farsightedness have eyes in which light is focused behind and have difficulty focusing on close objects. Besides miosis people may experience squinting to see better, difficulty with close tasks or burning sensation around your eyes.

